Home ≫Mortuary >Virtual Dissection Table and Digital Systems >3D Printing Models >3D Printing Model- General Embryo SMI-3DP-GE
Constructing a multi-structured 3D digital anatomical model using high-precision digitized human body data. A full-color, multi-material 3D printer and environmentally friendly resin materials are used to create 1:1 highly accurate simulations of physical anatomical models.
The texture features of the unevenness of the skull base are clearly visible. All the holes, fissures, and protrusions that enter and exit the skull are accurately preserved, including the sieve holes, rupture holes, spinous holes, carotid canals, and other structures. The flat, thin, and slender structures such as the sphenoid pterygoid process, pear bone, inferior turbinate, and styloid process are also displayed with precision. Anatomical features like the foramen ovale, petrous part of the temporal bone, grooves, fissures, protrusions, depressions, holes, impressions, and other markers are clearly defined and distinguishable.
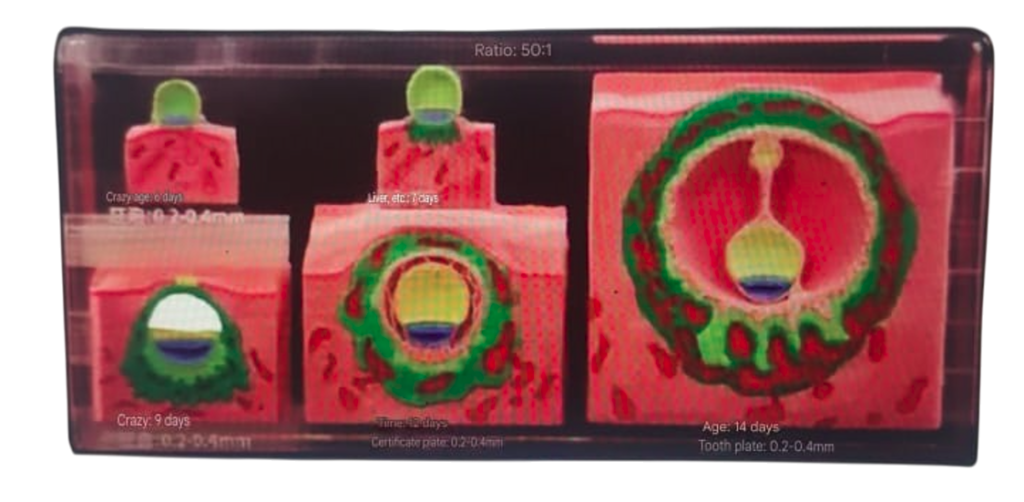
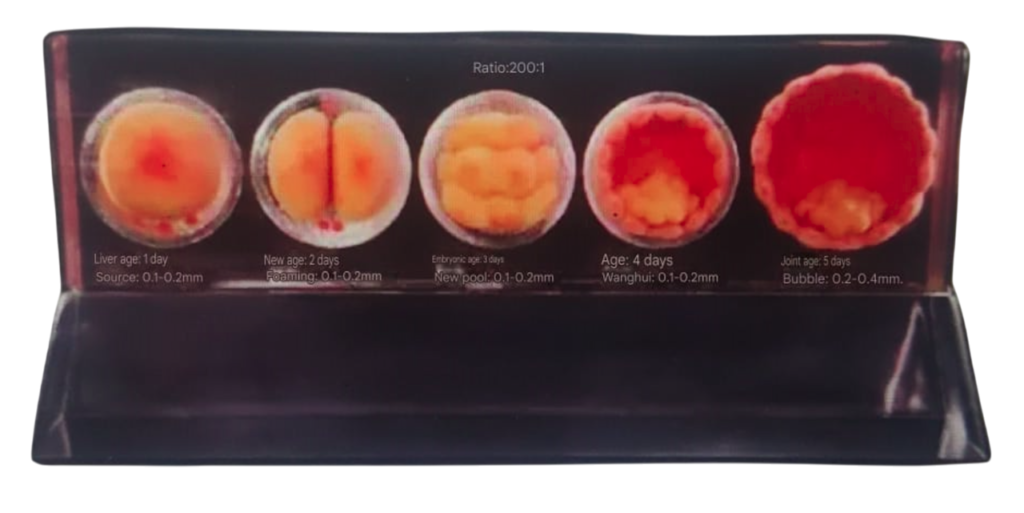

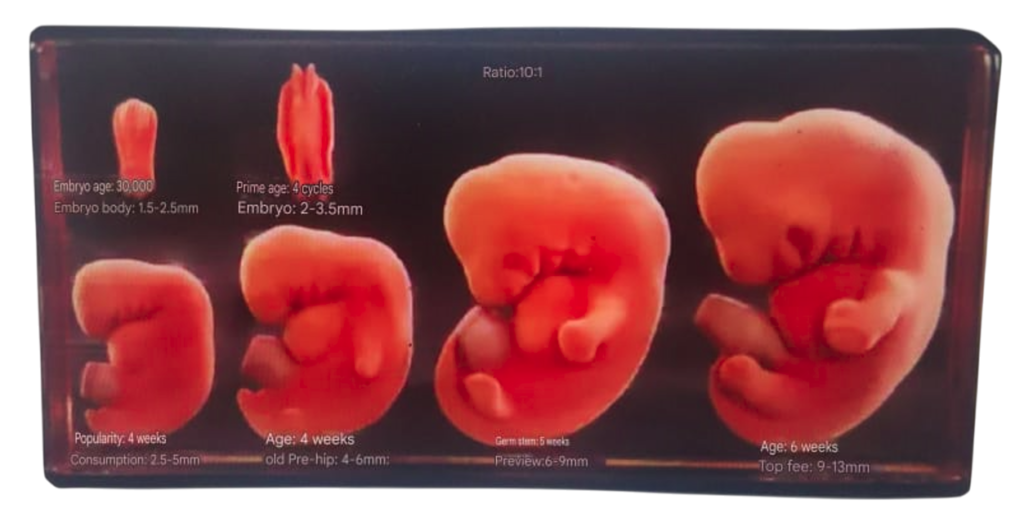
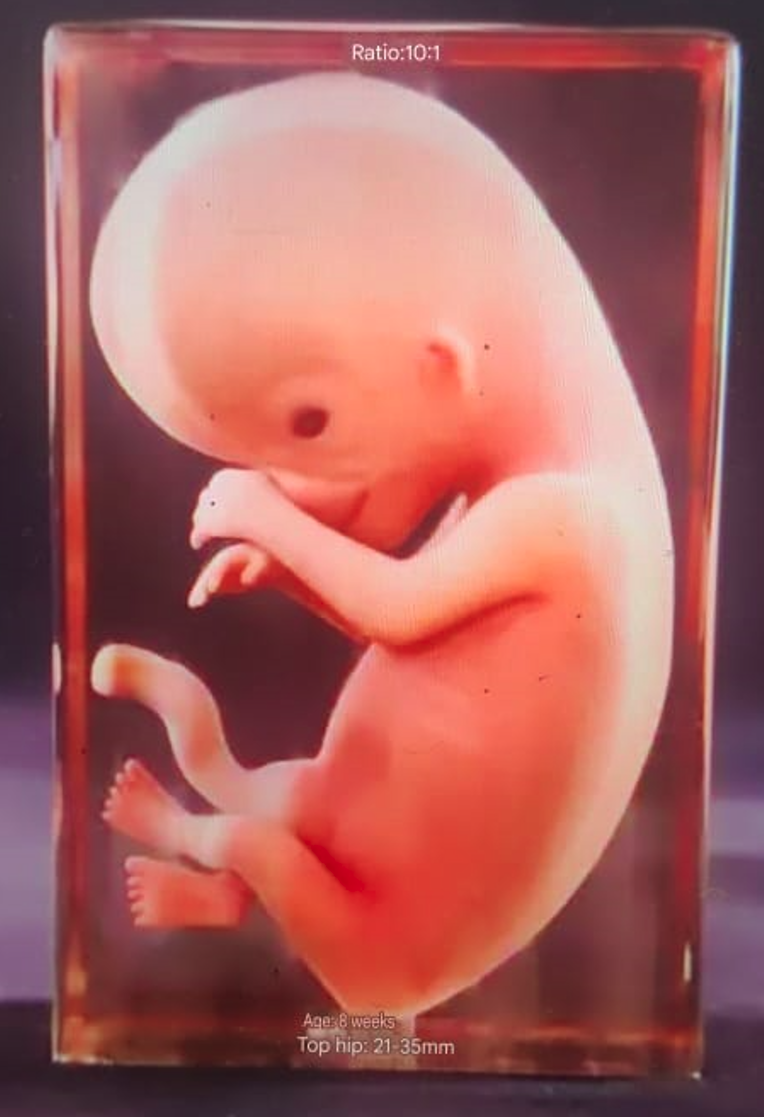
Physiological features: Separation of fingers (toes), growth of upper and lower extremities, formation of elbow and knee flexion, development of the five senses and facial features, disappearance of the tail, and the continued presence of the umbilical hernia.
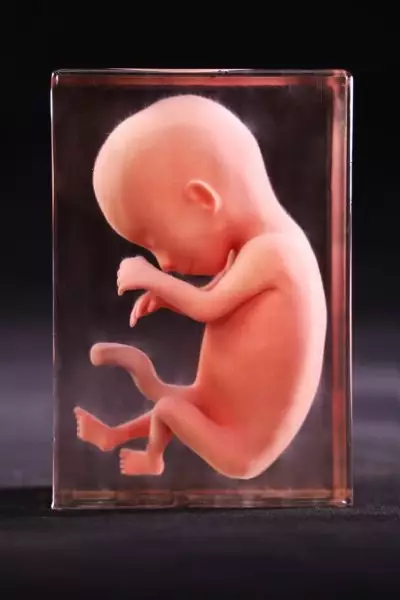
Physiological features: The physiological umbilical hernia disappears, the eyelids close, the sex of the external genitalia becomes recognizable, the eyes and ears approach their intrinsic position, and the nails and toenails appear successively.
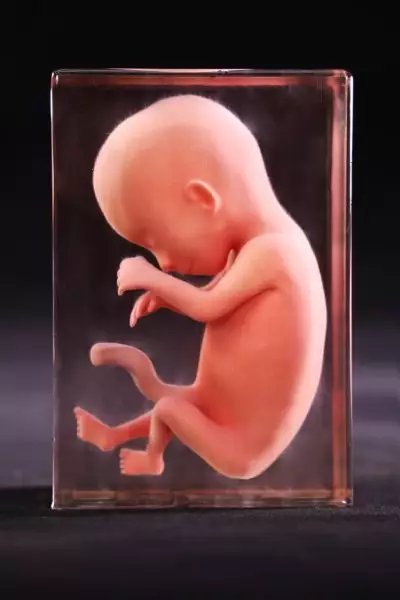
Physiological features: Fetal fat and hair appear, the eyelids remain closed, and the fetal body is emaciated.
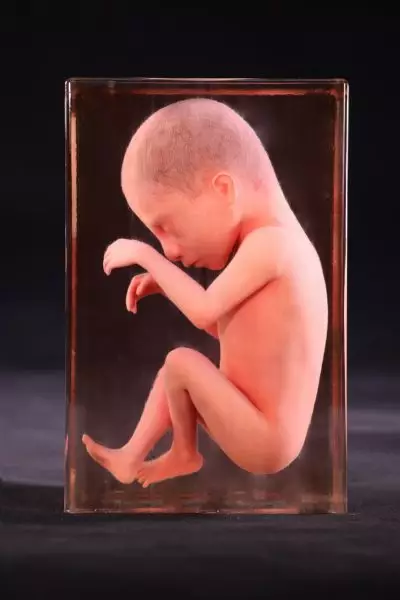

Physiological features: Appearance of eyebrows, opening of eyelids, growth of hair, appearance of eyelashes, disappearance of the pupillary membrane, and reduction of skin folds.
Data Source: Data were selected from a high-precision digital human dataset, including original sectional data, refined segmentation data, and 3D geometric models of organ structures, such as bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, and ligaments. The voxel size of this dataset is 0.0384 mm * 0.0384 mm * 0.1 mm. Formalin-fixed cadaveric specimens were also used as a reference and comparison basis for the 3D printing model.
Model Creation: The voxels on the surface of each anatomical structure in the volume data were extracted from the original sectional dataset, and texture maps of the geometric models were generated to ensure that the appearance of each anatomical structure’s geometric model aligns visually with the real anatomical specimen.
Product Brochure Link here